TORONTO, Feb. 22, 2022 – Aquatic birds are the most visibly affected organisms in an oil spill and a key measure of the environmental damage caused by them, such as the large spill off the coast of Peru last month. But accurately estimating how many birds have been affected requires pre-incident planning, says new research.
With almost 900 thousand tonnes of oil released into aquatic environments annually, pre-incident planning is critical to collecting pre-spill data and developing response plans.
“Preparations prior to spills help improve our understanding of the number of birds killed. The more pre-planning undertaken, the more robust the estimates will be,” says York University Professor Gail Fraser of the Faculty of Environmental and Urban Change and the corresponding author.
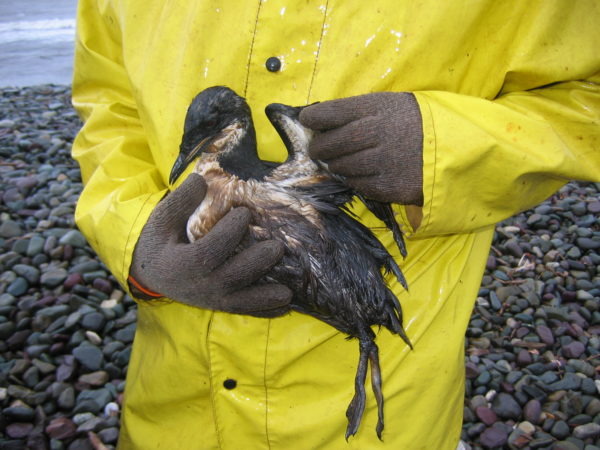

An oiled murre. Credit Environment and Climate Change Canada
Fraser, along with colleagues Research Scientist Greg Robertson of Environment and Climate Chante Canada, Director of the Marine Bird Program Iain Stenhouse of the Biodiversity Research Institute in Maine, and Senior Lecturer Joanne Ellis of the University of Waikato in New Zealand, has developed recommendations on how to best estimate the number of birds killed in an oil spill.
The research team emphasizes the importance of improving pre-incident planning that will assist in formulating response plans and estimating bird mortality.
“When environmental disasters, like an oil spill occur, the responses are complex and can involve many different agencies depending on the size and length of the spill. If no preparation or planning has occurred, the chaotic nature of the response may compromise the ability to estimate bird mortality,” says Fraser.
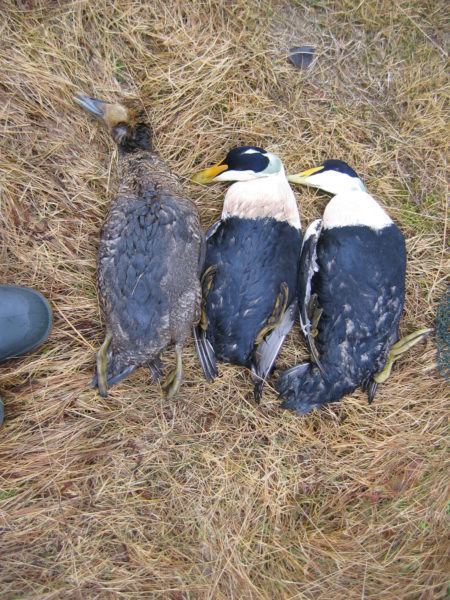

Oiled eiders. Credit Environment and Climate Change Canada
Pre-planning includes understanding whether oiled birds will reach coastlines or if the mortality estimates will be determined only by on-the-water sampling and identifying areas with high bird densities. In the event an incident occurs before quality data is obtained, the researchers have identified approaches that can be used during, or after, an incident.
The team also notes mortality estimates are of considerable public interest and may be used in subsequent legal proceedings, and to inform future disaster planning and mitigation.
“We cannot over emphasize the importance of improving pre-incident planning. It will assist in formulating response plans as well as improving the accuracy of bird mortality estimates,” says Stenhouse.
The paper, Estimating the numbers of aquatic birds affected by oil spills: Pre-planning, response, and post incident considerations, is published in the journal Environmental Reviews. (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/er-2021-0121)
-30-
York University is a modern, multi-campus, urban university located in Toronto, Ontario. Backed by a diverse group of students, faculty, staff, alumni and partners, we bring a uniquely global perspective to help solve societal challenges, drive positive change and prepare our students for success. York's fully bilingual Glendon Campus is home to Southern Ontario's Centre of Excellence for French Language and Bilingual Postsecondary Education. York’s campuses in Costa Rica and India offer students exceptional transnational learning opportunities and innovative programs. Together, we can make things right for our communities, our planet, and our future.
Media Contacts:
Sandra McLean, York University Media Relations, 416-272-6317, sandramc@yorku.ca
Gail Fraser, Faculty of Environmental and Urban Change, York University, gsfraser@yorku.ca