TORONTO, Thursday, June 29, 2017 – Worker and queen honeybees exposed to field realistic levels of neonicotinoids die sooner, reducing the health of the entire colony, a new study led by York University biologists has found.
The researchers were also surprised to find that the neonicotinoid contaminated pollen collected by the honeybees came not from crops grown from neonicotinoid treated seeds, but plants growing in areas adjacent to those crops.
The role of neonicotinoid insecticides in honeybee colony deaths in Ontario and other parts of North America has been controversial. Some critics dismissed studies that found negative effects on worker behavior and colony health as unrealistic, suggesting bees were exposed to higher doses of pesticides for much longer than realistically found in the field.
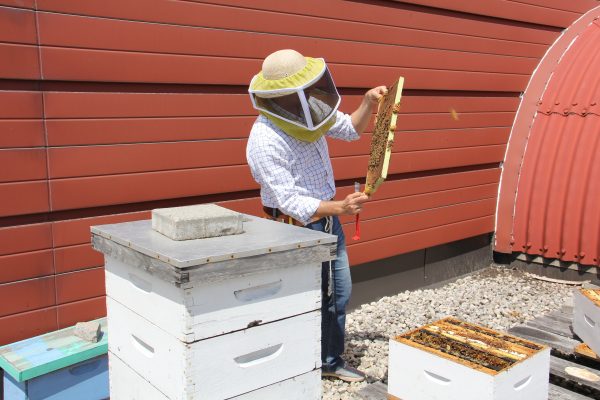

Professor Amro Zayed checking out a frame of honeybees from one of his rooftop colonies at York University
“This debate about field realistic exposure has been going on for a long time,” said York U biology Professor Amro Zayed of the Faculty of Science. “We needed season-long monitoring of neonics in bee colonies to determine the typical exposure scenarios that occur in the field, which we have now done.
The research team studied honey bee colonies in five apiaries close to corn grown from neonicotinoid-treated seeds and six apiaries that were far from agriculture. These colonies were extensively sampled and tested for pesticides from early May to September.
“Honeybee colonies near corn were exposed to neonicotinoids for three to four months. That is most of the active bee season in temperate North America,” said York U PhD student Nadia Tsvetkov.
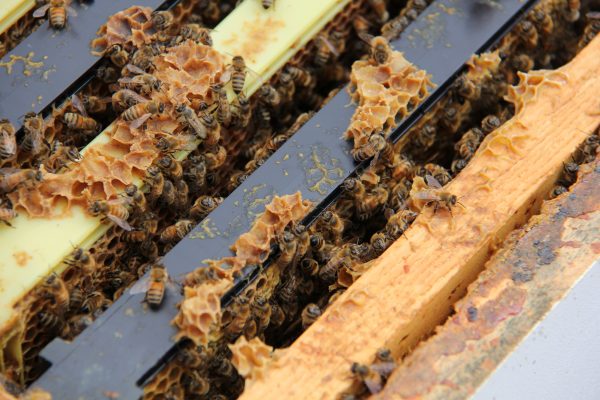

Worker honeybees in a hive at York University
However, the neonicotinoid contaminated pollen the honeybees collected did not belong to corn or soybean plants – the two primary crops grown from neonicotinoid treated seeds in Ontario and Quebec.
“This indicates that neonicotinoids, which are water soluble, spill over from agricultural fields into the surrounding environment, where they are taken up by other plants that are very attractive to bees,” said Tsvetkov.
The researchers then chronically fed colonies with an artificial pollen supplement containing progressively smaller amounts of the most commonly used neonicotinoid in Ontario, clothianidin, over a 12-week period. The experiment mimicked what would occur naturally in the field.
The worker bees exposed to the treated pollen during the first nine days of life had their lifespans cut short by 23 per cent. Colonies that were exposed to treated pollen were unable to maintain a healthy laying queen, and had poor hygiene. “We found that realistic exposure to neonicotinoids near corn fields reduces the health of honey bee colonies,” said Tsvetkov.
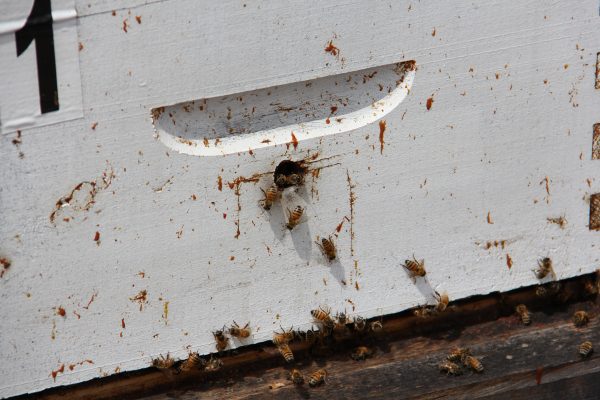

Honeybees going in and out of hive at York University
While chronic exposure to neonicotinoids has negative effects on honeybees, the researchers also discovered that a commonly used fungicide can interact with neonicotinoids to make them more dangerous.
“The effect of neonicotinoids on honey bees quickly turns from bad to worse when you add the fungicide boscalid to the mix,” said Professor Valérie Fournier of Laval University who collaborated with the York U team. “The researchers found that field realistic levels of boscalid can make neonicotinoids twice as toxic to honeybees.”
The research, “Chronic exposure to neonicotinoids reduces honeybee health near corn crops,” is published today in the journal Science.
-30-
York University is known for championing new ways of thinking that drive teaching and research excellence. Our students receive the education they need to create big ideas that make an impact on the world. Meaningful and sometimes unexpected careers result from cross-discipline programming, innovative course design and diverse experiential learning opportunities. York students and graduates push limits, achieve goals and find solutions to the world’s most pressing social challenges, empowered by a strong community that opens minds. York U is an internationally recognized research university – our 11 faculties and 26 research centres have partnerships with 200+ leading universities worldwide. Located in Toronto, York is the third largest university in Canada, with a strong community of 53,000 students, 7,000 faculty and administrative staff, and more than 295,000 alumni. York U's fully bilingual Glendon campus is home to Southern Ontario's Centre of Excellence for French Language and Bilingual Postsecondary Education.
Media Contact:
Sandra McLean, York University Media Relations, 416-736-2100 ext. 22097, sandramc@yorku.ca